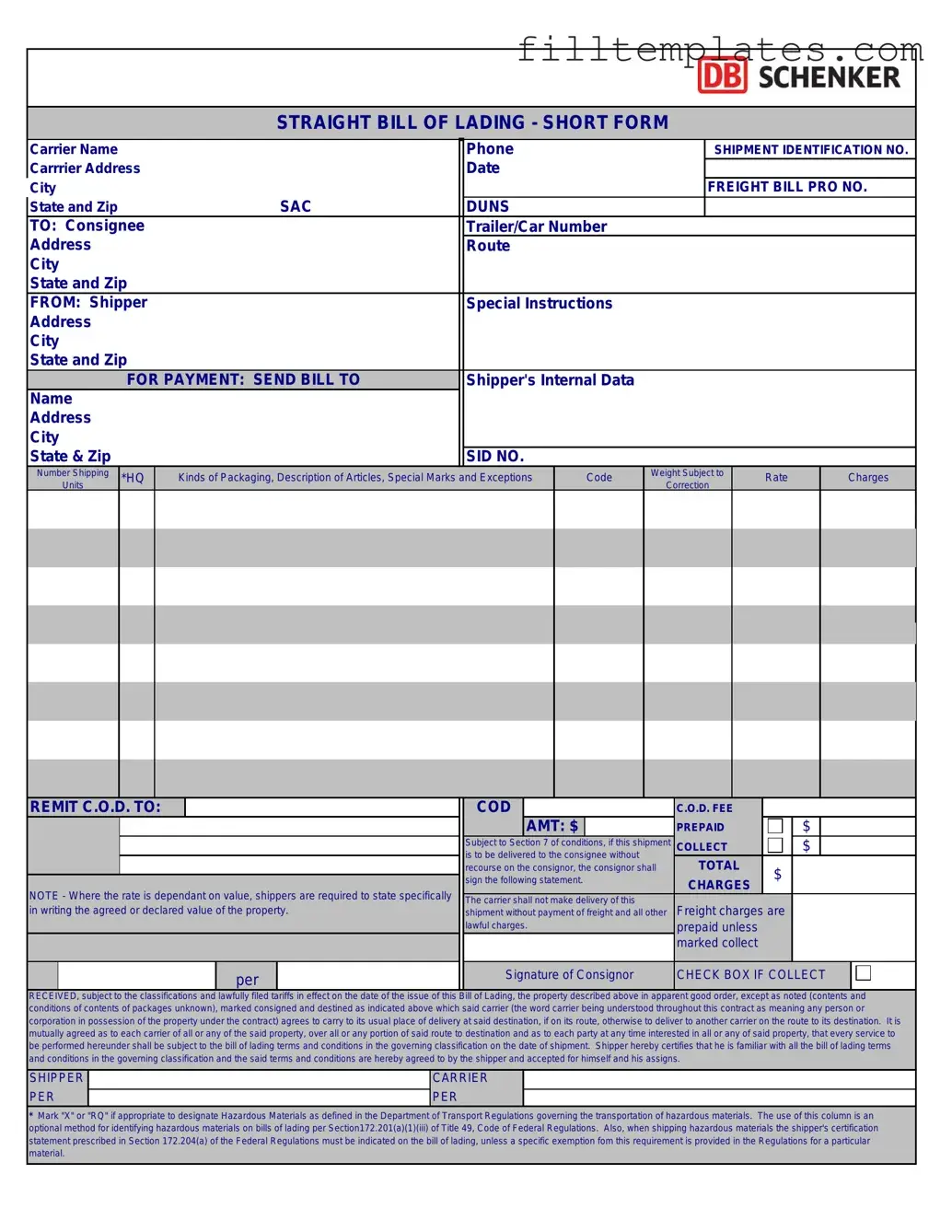
Download Straight Bill Of Lading Template
The Straight Bill of Lading is a crucial document in the shipping and transportation industry, serving as a receipt for goods and a contract between the shipper and the carrier. This form is typically used when the goods are consigned directly to a specific individual or entity, ensuring that only the named consignee can claim the shipment upon arrival. Unlike other types of bills of lading, the Straight Bill does not allow for the transfer of ownership or endorsement, making it a non-negotiable instrument. It contains essential details such as the names and addresses of the shipper and consignee, a description of the goods being transported, and any special instructions for handling the shipment. Additionally, it often includes information about the freight charges and the terms of delivery. Understanding the Straight Bill of Lading is vital for anyone involved in logistics, as it helps to streamline the shipping process and provides legal protection in case of disputes or damage during transit.
Key takeaways
When filling out and using the Straight Bill of Lading form, consider the following key takeaways:
- Accurate Information: Ensure all details, including names, addresses, and descriptions of goods, are correct to avoid delays.
- Signature Requirement: The bill must be signed by the shipper or their authorized representative to be valid.
- Terms and Conditions: Review the terms and conditions outlined on the bill. They govern the transportation agreement.
- Document Retention: Keep a copy of the signed bill for your records. This serves as proof of shipment.
- Carrier Responsibilities: Understand the carrier's obligations regarding the transport of goods as detailed in the bill.
- Delivery Instructions: Clearly state any special delivery instructions to ensure proper handling upon arrival.
- Liability Limitations: Be aware of any limitations on liability for loss or damage to the goods during transit.
- Use of Multiple Copies: Distribute multiple copies of the bill to relevant parties, including the shipper, carrier, and consignee.
Guide to Writing Straight Bill Of Lading
Filling out the Straight Bill of Lading form is a straightforward process that requires careful attention to detail. This document is essential for shipping goods and serves as a receipt for the shipment. Follow these steps to ensure accuracy and completeness.
- Shipper Information: Enter the name, address, and contact information of the person or company sending the shipment.
- Consignee Information: Fill in the name, address, and contact details of the recipient who will receive the shipment.
- Carrier Information: Provide the name of the transportation company that will be handling the shipment.
- Shipment Details: Describe the items being shipped. Include the quantity, weight, and any special handling instructions.
- Freight Charges: Indicate whether the freight charges will be prepaid or collected upon delivery.
- Signature: The shipper must sign and date the form to confirm that all information is accurate and complete.
Once the form is filled out, keep a copy for your records. Ensure that all parties involved have the necessary information to track and manage the shipment effectively.
Browse Other PDFs
Drivers Time Record Sheet - Completion of this form contributes to maintaining proper records for workplace compliance.
For those seeking a reliable legal tool, the effective Room Rental Agreement template is vital in managing rental relationships. This document plays a key role in establishing a clear understanding between landlords and tenants, ensuring all parties are on the same page regarding their obligations and rights.
Geico Vendor Online Services - This form is part of maintaining a professional relationship with GEICO.
Form Preview Example
STRAIGHT BILL OF LADING - SHORT FORM
Carrier Name |
|
|
Phone |
|
|
SHIPMENT IDENTIFICATION NO. |
||
Carrrier Address |
|
|
Date |
|
|
|
|
|
City |
SAC |
|
|
|
|
FREIGHT BILL PRO NO. |
||
State and Zip |
|
DUNS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TO: Consignee |
|
|
Trailer/Car Number |
|
|
|
|
|
Address |
|
|
Route |
|
|
|
|
|
City |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
State and Zip |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FROM: Shipper |
|
|
Special Instructions |
|
|
|
|
|
Address |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
City |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
State and Zip |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FOR PAYMENT: SEND BILL TO |
|
Shipper's Internal Data |
|
|
|
|
||
Name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Address |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
City |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
State & Zip |
|
|
SID NO. |
|
|
|
|
|
Number Shipping *HQ |
Kinds of Packaging, Description of Articles, Special Marks and Exceptions |
Code |
Weight Subject to |
Rate |
Charges |
|||
Units |
|
|
|
|
Correction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
REMIT C.O.D. TO: |
|
|
|
|
COD |
|
|
C.O.D. FEE |
|
|
|
|
||
Address |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AMT: $ |
|
PREPAID |
|
$ |
|
|
|
City |
|
|
|
|
|
Subject to Section 7 of conditions, if this shipment |
COLLECT |
|
$ |
|
|
|||
State & Zip |
|
|
|
|
|
is to be delivered to the consignee without |
TOTAL |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
recourse on the consignor, the consignor shall |
$ |
|
|
|
|||||
NOTE - Where the rate is dependant on value, shippers are required to state specifically |
|
sign the following statement. |
CHARGES |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
The carrier shall not make delivery of this |
Freight charges are |
|
|
|
|||||||||
in writing the agreed or declared value of the property. |
|
shipment without payment of freight and all other |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
lawful charges. |
prepaid unless |
|
|
|
|
||
The agreed or declared vlaue of the property is hereby specifically stated by the shipper to |
|
|
|
|
marked collect |
|
|
|
|
|||||
be not exceeding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
$ |
|
|
|
per |
|
|
Signature of Consignor |
CHECK BOX IF COLLECT |
|
|||||
RECEIVED, subject to the classifications and lawfully filed tariffs in effect on the date of the issue of this Bill of Lading, the property described above in apparent good order, except as noted (contents and conditions of contents of packages unknown), marked consigned and destined as indicated above which said carrier (the word carrier being understood throughout this contract as meaning any person or corporation in possession of the property under the contract) agrees to carry to its usual place of delivery at said destination, if on its route, otherwise to deliver to another carrier on the route to its destination. It is mutually agreed as to each carrier of all or any of the said property, over all or any portion of said route to destination and as to each party at any time interested in all or any of said property, that every service to be performed hereunder shall be subject to the bill of lading terms and conditions in the governing classification on the date of shipment. Shipper hereby certifies that he is familiar with all the bill of lading terms and conditions in the governing classification and the said terms and conditions are hereby agreed to by the shipper and accepted for himself and his assigns.
SHIPPER |
|
CARRIER |
|
PER |
|
PER |
|
*Mark "X" or "RQ" if appropriate to designate Hazardous Materials as defined in the Department of Transport Regulations governing the transportation of hazardous materials. The use of this column is an optional method for identifying hazardous materials on bills of lading per Section172.201(a)(1)(iii) of Title 49, Code of Federal Regulations. Also, when shipping hazardous materials the shipper's certification statement prescribed in Section 172.204(a) of the Federal Regulations must be indicated on the bill of lading, unless a specific exemption fom this requirement is provided in the Regulations for a particular material.
Documents used along the form
The Straight Bill of Lading is a crucial document in the shipping and transportation industry, serving as a receipt for goods and a contract between the shipper and carrier. However, it is often accompanied by other important forms and documents that facilitate the smooth movement of goods. Below is a list of commonly used documents that complement the Straight Bill of Lading.
- Commercial Invoice: This document details the transaction between the buyer and seller, including the price, quantity, and description of the goods. It serves as a crucial record for customs clearance and payment processing.
- Packing List: A packing list outlines the contents of each package, including weights and dimensions. This document helps ensure that the correct items are shipped and received, and it aids in inventory management.
- Certificate of Origin: This certificate verifies the country in which the goods were manufactured. It is often required for customs clearance and can affect tariffs and duties.
- FedEx Bill of Lading: The OnlineLawDocs.com provides resources to understand this important document used in the shipping industry that details the terms, conditions, and particulars of a shipment.
- Import/Export License: This license is necessary for businesses involved in international trade. It ensures that the company is authorized to import or export specific goods, complying with government regulations.
- Insurance Certificate: This document provides proof of insurance coverage for the goods during transit. It protects the shipper and receiver against potential losses or damages.
- Delivery Receipt: A delivery receipt is signed by the recipient upon receiving the goods. It serves as proof that the items were delivered in satisfactory condition.
- Freight Bill: This bill outlines the charges associated with the transportation of goods. It includes details such as weight, distance, and the agreed-upon rate for shipping services.
- Customs Declaration: This document is submitted to customs authorities to declare the contents of a shipment. It includes details about the goods, their value, and their intended use, ensuring compliance with import/export regulations.
- Warehouse Receipt: A warehouse receipt serves as proof of storage for goods held in a warehouse. It can be used to transfer ownership or as collateral for financing.
Understanding these documents is essential for anyone involved in shipping and logistics. Each plays a vital role in ensuring compliance, protecting interests, and facilitating smooth transactions. Be proactive in gathering and managing these documents to avoid potential delays and complications in the shipping process.